The C_CORRELATE function computes the cross correlation Pxy(L) or biased cross covariance Rxy(L) of two sample populations X and Y as a function of the lag L
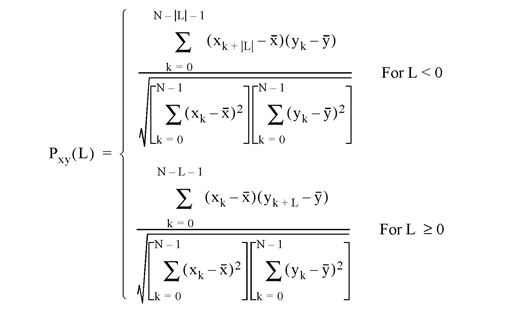
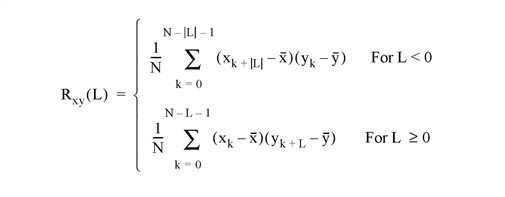
where x and y are the means of the sample populations x = (x0, x1, x2, ... , xN-1) and y = (y0, y1, y2, ... , yN-1), respectively.
This routine is written in the IDL language. Its source code can be found in the file c_correlate.pro in the lib subdirectory of the IDL distribution.
Examples
X = [3.73, 3.67, 3.77, 3.83, 4.67, 5.87, 6.70, 6.97, 6.40, 5.57]
Y = [2.31, 2.76, 3.02, 3.13, 3.72, 3.88, 3.97, 4.39, 4.34, 3.95]
lag = [-5, 0, 1, 5, 6, 7]
result = C_CORRELATE(X, Y, lag)
PRINT, result
IDL prints:
-0.428246 0.914755 0.674547 -0.405140 -0.403100 -0.339685
Syntax
Result = C_CORRELATE( X, Y, Lag [, /COVARIANCE] [, /DOUBLE] )
Return Value
Returns the cross correlation Pxy(L) or cross covariance Rxy(L) of two sample populations X and Y as a function of the lag L.
Arguments
X
An n-element integer, single-, or double-precision floating-point vector.
Y
An n-element integer, single-, or double-precision floating-point vector.
Lag
A scalar or n-element integer vector in the interval [-(n-2), (n-2)], specifying the signed distances between indexed elements of X.
Keywords
COVARIANCE
Set this keyword to compute the sample cross covariance rather than the sample cross correlation.
DOUBLE
Set this keyword to force the computation to be done in double-precision arithmetic.
Version History
Resources and References
Wayne A. Fuller, Introduction to Statistical Time Series, Wiley-Interscience, December 1995 (ISBN 978-0471552390).
See Also
A_CORRELATE, CORRELATE, M_CORRELATE, P_CORRELATE, R_CORRELATE